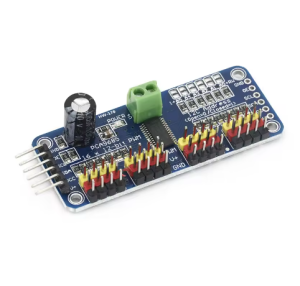
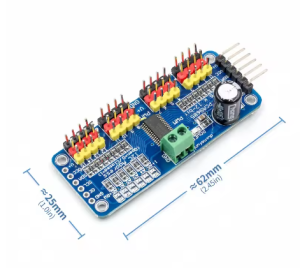
- 16 Independent Channels: Provides 16 dedicated PWM outputs, each with its own independent ON/OFF time and duty cycle control.
- I²C Communication: Uses only two I/O pins (SDA, SCL) to control all 16 channels, freeing up valuable microcontroller pins.
- Integrated Clock: Built-in 25 MHz internal oscillator means no continuous signal is needed from the host microcontroller, reducing overhead.
- High Resolution: Offers 12-bit (4096 steps) resolution for each channel for precise control.
- Adjustable Frequency: Programmable PWM frequency range from 24 Hz to 1526 Hz.
- Wide Compatibility: 5V compliant inputs/outputs allow control from 3.3V microcontrollers (like Raspberry Pi) while safely driving up to 6V outputs for LEDs or servos.
- Chainable Design: Up to 62 modules can be connected in series on a single I²C bus, offering massive scalability for large projects (up to 992 outputs).
- External Power Input: Features a terminal block for a separate external power source (e.g., 5-6V for servos) to handle high current requirements with reverse polarity protection.
- Pre-Soldered Pins: Comes with all necessary header pins pre-soldered for ease of use and quick setup.
- Output Protection: Each PWM output line has a 220-ohm series resistor for protection and ease of driving LEDs.
PCA9685 16-Channel PWM Servo Motor Controller Board (Pre-Soldered Pins)
| Driver Chip | PCA9685 |
|---|---|
| Logic Voltage (VCC) | 2.3V to 5.5V |
| External Power (V+) | Up to 6V (typically 5V for servos) |
| Communication Interface | I²C (Fast-mode Plus, up to 1 MHz) |
| Channels | 16 independent PWM channels |
| Resolution | 12-bit (4096 steps) |
| Frequency Range | 24 Hz to 1526 Hz (typical default 200 Hz) |
| Output Current per Channel | 25 mA (sink), 10 mA (source) at 5V |
| Max Addressable Modules | 62 (via A0-A5 pins) |
| Dimensions | Approx. 62.5mm x 25.4mm x 3mm (board only) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
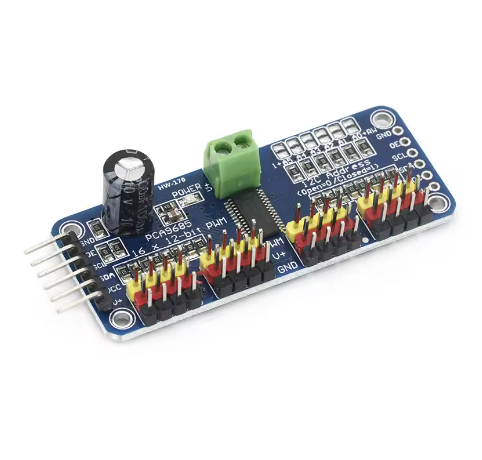
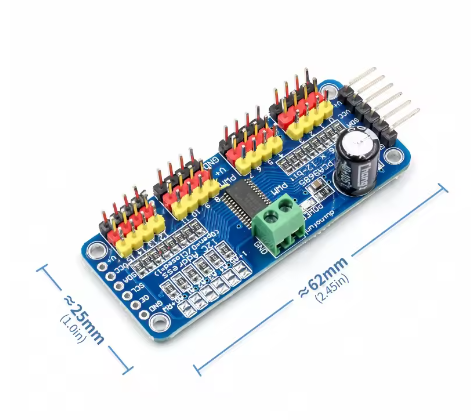
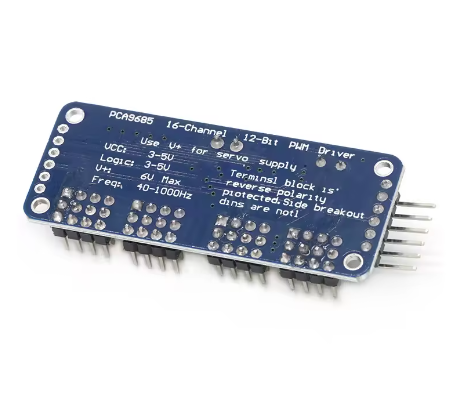
- Connections:
- Connect the VCC pin to your microcontroller’s logic power supply (3.3V or 5V).
- Connect the GND pin to the common ground of your system and external power supply.
- Connect the SDA and SCL pins to your microcontroller’s I²C data and clock lines, respectively.
- Connect a separate, regulated power supply (typically 5-6V for servos) to the V+ terminal block (or pin) to power the attached servos or LEDs.
- Configuration:
- The board has a default I²C address of
0x40. For multiple boards, use the address selection solder pads (A0-A5) to assign unique addresses to each board (up to 62 total).
- The board has a default I²C address of
- Programming:
- Use a compatible library for your chosen platform (e.g., Adafruit PWM Servo Driver library for Arduino/CircuitPython, or relevant libraries for Raspberry Pi or ESP32).
- Initialize the library and set the desired PWM frequency (50-60 Hz is standard for servos).
- Use the library functions to set the pulse width (or angle, depending on the library) for each channel to control the connected device.
The board is primarily used to control up to 16 servos or LEDs simultaneously when the main microcontroller has insufficient PWM output pins.
It is generally not recommended to power multiple servos directly from your microcontroller’s 5V pin, as servos draw significant current and can cause power issues or brownouts. Use a separate, dedicated external power supply connected to the V+ pin
The PCA9685 offers 12-bit resolution, which provides 4096 individual steps of control for each channel. This allows for very fine and precise control over the position of a servo or the brightness of an LED
Yes, you can. However, all outputs on the PCA9685 share the same PWM frequency. Servos typically require a frequency of around 50-60 Hz, while LEDs can benefit from higher frequencies (e.g., 1000 Hz) to avoid flicker. You must set the board to a single, consistent frequency for all channels
The board has 6 address selection pins, allowing you to chain up to 62 modules on the same I²C bus, controlling a maximum of 992 PWM outputs. Each board must be assigned a unique I²C address via the solder pads