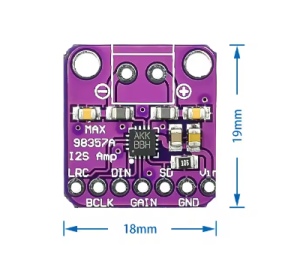
- Digital I2S Input: Accepts standard I2S digital audio data, eliminating the need for bulky analog audio lines and reducing noise.
- Filterless Class D Architecture: Patented design allows direct speaker connection without large output filters, saving space and complexity.
- High Power Output: Delivers up to 3 Watts of clear, mono audio power into a 4Ω load.
- Wide Operating Voltage: Operates efficiently from a single 2.7V to 5.5V DC supply.
- Flexible Data Formats: Supports 16-bit, 20-bit, or 24-bit I2S data in standard left-justified, right-justified, and TDM formats.
- Adjustable Gain: Configurable gain settings (3dB, 6dB, 9dB, 12dB, 15dB) via the GAIN pin for output level matching.
- Integrated Protections: Includes thermal shutdown and short-circuit protection for robust and safe operation.
- Compact Design: Extremely small form factor (approx. 20 mm x 20 mm) ideal for portable and space-constrained applications
MAX98357 I2S Digital Audio Amplifier Module – Filterless Class D Amp Board for ESP32, Raspberry Pi (Pi 3/4/Zero), Arduino
| Amplifier IC | MAX98357A / MAX98357B |
|---|---|
| Amplifier Class | D (Filterless) |
| Channels | Mono (Single) |
| Operating Voltage | 2.7V – 5.5V DC |
| Max Output Power | 3W (into 4Ω load at 5V supply) |
| Sample Rates | 8kHz to 96kHz |
| Digital Audio Interface | I2S (Input Only) |
| Bit Depth Support | 16/20/24-bit |
| Input Formats | Standard I2S, Left-Justified, Right-Justified, TDM |
| Dimensions (L x W) | Approx. 20 x 20 mm |
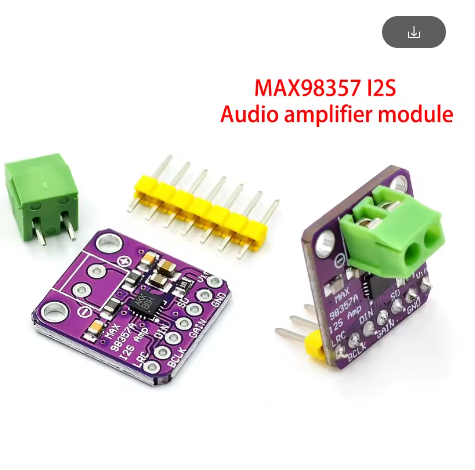
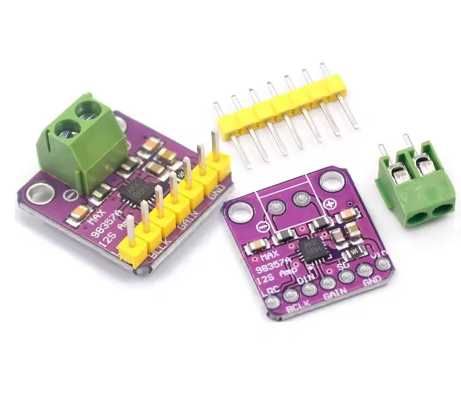
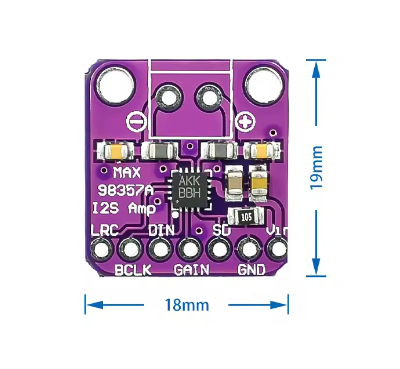




- VCC: Connect to a 2.7V to 5.5V DC power supply (5V is common for Raspberry Pi/ESP32).
- GND: Connect to the common ground of your system and power supply.
- BCLK (Bit Clock): Connect to the BCLK pin of your host device (e.g., GPIO18 on Raspberry Pi 3/4).
- LRCK (Left/Right Clock or Frame Clock): Connect to the LRCK pin of your host device (e.g., GPIO19 on Raspberry Pi 3/4).
- DIN (Digital Input Data): Connect to the DIN/DOUT pin of your host device (e.g., GPIO21 on Raspberry Pi 3/4).
- GAIN: This pin controls the gain. Connect to VCC, GND, or float it (depending on the specific IC version A/B) to select one of the five gain settings. Refer to the MAX98357 datasheet for specific GAIN pin configurations.
- SD (Shutdown): Connect to GND to shut down the amplifier (low power mode). Connect to VCC or float it for normal operation.
- Speaker Connections: Connect a 4Ω to 8Ω speaker directly to the designated speaker terminal block. Polarity is important for optimal sound.
- IoT Voice Projects: Adding voice assistants or notification sounds to smart home devices (ESP32 is commonly used).
- Raspberry Pi Audio Out: A high-quality alternative to the 3.5mm jack or HDMI audio on the Raspberry Pi Zero, 3, and 4.
- Custom Audio Players: Building compact digital audio players with microcontrollers.
- Educational Platforms: Ideal for robotics and electronics education requiring simple digital audio output.
No, this module provides mono (single channel) audio output. For stereo sound, you would need two separate modules (one configured for the left channel and one for the right channel)
No, the standard Arduino Uno does not natively support an I2S interface. You need a microcontroller with dedicated I2S pins, such as the ESP32, ESP8266 (requires library workarounds), Arduino Due, or Teensy boards
The primary difference lies in how the GAIN pin selects the gain settings and potentially the default channel (A typically defaults to right channel data, B to left channel data on the DIN line). Both offer the same power output and core features. You should check which specific IC version you are using if you are struggling with channel selection in software
This module is filterless. No external output filter is required between the amplifier and the speaker. Standard decoupling capacitors are already integrated on the board itself.
On the Raspberry Pi OS, you typically need to enable the I2S overlay (dtoverlay=hifiberry-dac or similar in /boot/config.txt) and select the appropriate sound output device in the system settings or via raspi-config