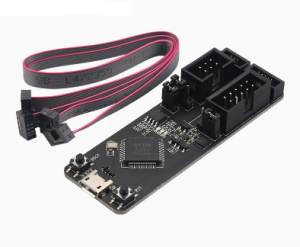
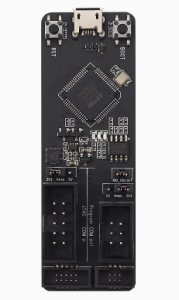
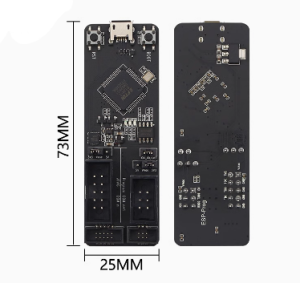
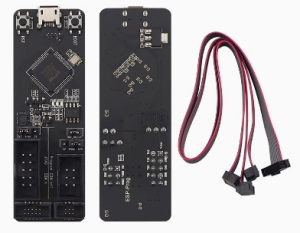
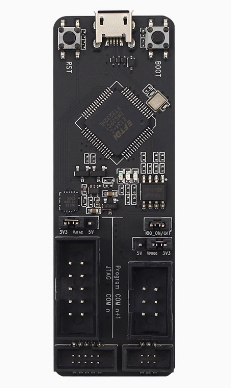
- Dual-Channel Versatility: One channel for Program Download (UART) and one for Hardware Debugging (JTAG).
- Universal Compatibility: Fully supports the entire Espressif range, including ESP8266, ESP32, ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3, and ESP32-C series.
- One-Click Flashing: Features automatic bootloader pin control (IO0 and EN), eliminating the need for manual button pressing during firmware uploads.
- Adjustable Logic Levels: Includes onboard jumpers to switch between 3.3V and 5V power supply and signal logic to match your target board.
- Standardized Headers: Uses 2.54mm pitch connectors for easy connection via jumper wires or standard IDC cables.
ESP-Prog Universal JTAG Debugger Highlights versatility for both ESP8266/ESP32
| Main Controller | FTDI FT2232HL |
|---|---|
| Interface | USB 2.0 High Speed (Micro-USB Connector) |
| Debugging Interface | JTAG (Standard Pins) |
| Programming Interface | UART (Serial) |
| Logic Voltage | 3.3V / 5V (Selectable via Jumpers) |
| Target Power Output | Up to 500mA |
| Compatible Software | OpenOCD, ESP-IDF, GDB, Arduino IDE, PlatformIO |
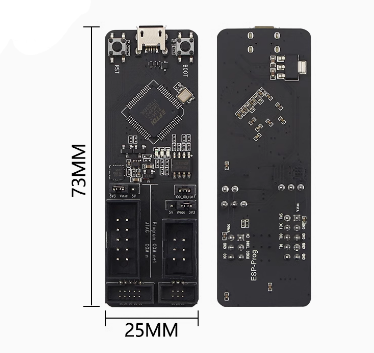
| Dimensions | 73.4mm x 25.1mm |
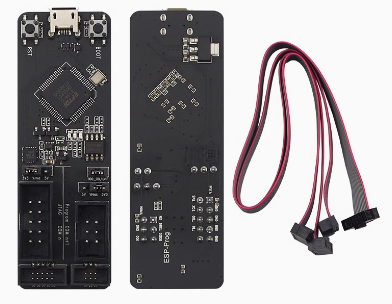
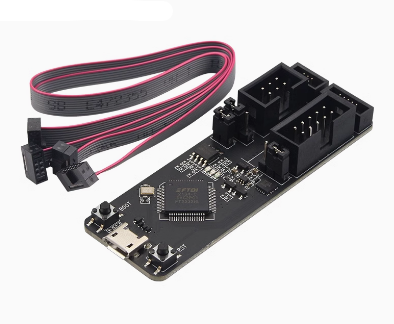
- Hardware Connection: Connect the ESP-Prog to your computer using a Micro-USB data cable.
- Cable Wiring: Connect the JTAG/UART pins of the ESP-Prog to the corresponding pins on your ESP32 or ESP8266 board (refer to your specific chip’s pinout for JTAG pins like TDI, TDO, TCK, TMS).
- Driver Installation: Install the FTDI drivers. For JTAG functionality on Windows, you may need to use Zadig to switch the driver for Channel 0 to “WinUSB”.
- Debugging in ESP-IDF:
- Set your interface to
board/esp32-wrover-kit.cfg(which uses the same FT2232 layout). - Run
idf.py gdbguioridf.py monitorfor real-time analysis.
- Set your interface to
- Voltage Selection: Before connecting, ensure the onboard jumper matches your target board’s voltage (typically 3.3V).
Yes, for firmware downloading, it works perfectly as a standard USB-to-Serial converter. However, the JTAG debugging features are best utilized in professional environments like VS Code with ESP-IDF or PlatformIO.
While the ESP-Prog supports the ESP8266 UART for programming, please note that the ESP8266 has limited hardware JTAG support compared to the ESP32. Most users use the ESP-Prog’s JTAG features specifically for the ESP32 series
The board is split into two functional areas. The Program header is for standard Serial communication (TX/RX/Reset/Boot), and the JTAG header is for advanced hardware debugging
Yes! The FT2232HL is a dual-port chip. Port A is generally used for JTAG and Port B is used for UART (Serial) communication
The ESP-Prog can provide power to your target board via the VCC pins. However, for power-hungry projects (like those using Wi-Fi and motors), it is recommended to power the target board via its own source and only connect the Ground (GND) and signal pins to the ESP-Prog
No, most development boards have a built-in USB-to-Serial chip. This tool is an upgrade for boards that lack an onboard USB port or for developers who need hardware-level debugging capabilities